From cTuning.org
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<div align="center">http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/ctuning_services.gif</div> | <div align="center">http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/ctuning_services.gif</div> | ||
| - | Collective Optimization Database (cDatabase or COD) provides a common global repository with data analysis plugins to share, analyze and reference useful program/architecture optimization cases. It has been developed to help users optimize programs, libraries, kernels and the whole systems (compiler optimizations/architecture configurations to improve execution time, code size, architecture size, power consumption, etc). It is intended to simplify and automate the design and optimization of programs, compilers, run-time systems and architectures based on recent statistical and machine learning techniques ({{Ref|FT2009}}, {{Ref|FMTP2008}}, {{Ref|ABCP2006}}, [http://cTuning.org/project-milepost MILEPOST], [http://unidapt.org UNIDAPT]). We also hope that it will also be useful for adaptive parallelization and scheduling for the emerging and future heterogeneous multi-core systems including current CPU/GPU and CELL architectures ([http://fursin.net/wiki/index.php5?title=Research:Dissemination#LCWP2009 LCWP2009]). Finally, it is intended to improve the quality of academic research by avoiding costly duplicate experiments and providing replicable referable results. It can provide detailed performance analysis and comparison of different programs, datasets, compilers and architectures. It can be used to optimize programs on-the-fly when using cloud computing services. | + | Collective Optimization Database (cDatabase or COD) provides a common global repository with data analysis plugins to share, analyze and reference useful program/architecture optimization cases. It has been developed to help users optimize programs, libraries, kernels and the whole systems (compiler optimizations/architecture configurations to improve execution time, code size, architecture size, power consumption, etc). It is intended to simplify and automate the design and optimization of programs, compilers, run-time systems and architectures based on recent statistical and machine learning techniques ({{Ref|FT2010}}, {{Ref|FT2009}}, {{Ref|FMTP2008}}, {{Ref|ABCP2006}}, [http://cTuning.org/project-milepost MILEPOST], [http://unidapt.org UNIDAPT]). We also hope that it will also be useful for adaptive parallelization and scheduling for the emerging and future heterogeneous multi-core systems including current CPU/GPU and CELL architectures ([http://fursin.net/wiki/index.php5?title=Research:Dissemination#LCWP2009 LCWP2009]). Finally, it is intended to improve the quality of academic research by avoiding costly duplicate experiments and providing replicable referable results. It can provide detailed performance analysis and comparison of different programs, datasets, compilers and architectures. It can be used to optimize programs on-the-fly when using cloud computing services. |
We currently keep information about architectures and their configurations, software environments, programs, datasets, compilers (such as GCC, Open64, ICC, PathScale and plan to add dynamic compilers such as LLVM, IBM Testerossa, etc), compiler flags for program and architecture optimizations, compiler [[CTools:ICI|ICI]] optimization passes, fine-grain program optimizations, execution time, code size, profiling statistics, program static and dynamic features (hardware counters), parallelization schemes, etc. | We currently keep information about architectures and their configurations, software environments, programs, datasets, compilers (such as GCC, Open64, ICC, PathScale and plan to add dynamic compilers such as LLVM, IBM Testerossa, etc), compiler flags for program and architecture optimizations, compiler [[CTools:ICI|ICI]] optimization passes, fine-grain program optimizations, execution time, code size, profiling statistics, program static and dynamic features (hardware counters), parallelization schemes, etc. | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
*'''2009.September.1''' - The documentation of [http://ctuning.org/milepost-gcc MILEPOST GCC]/[http://ctuning.org/ici GCC ICI] extensions by Yuanjie and Liang during GSOC'09 program is now available: [http://ctuning.org/wiki/index.php/CTools:ICI:Projects:GSOC09:Function_cloning_and_program_instrumentation Function cloning and program instrumentation] and [http://ctuning.org/wiki/index.php/CTools:ICI:Projects:GSOC09:Fine_grain_tuning Fine grain program tuning]. We would like to fully test and sync these developments with mainline GCC within next month or two. | *'''2009.September.1''' - The documentation of [http://ctuning.org/milepost-gcc MILEPOST GCC]/[http://ctuning.org/ici GCC ICI] extensions by Yuanjie and Liang during GSOC'09 program is now available: [http://ctuning.org/wiki/index.php/CTools:ICI:Projects:GSOC09:Function_cloning_and_program_instrumentation Function cloning and program instrumentation] and [http://ctuning.org/wiki/index.php/CTools:ICI:Projects:GSOC09:Fine_grain_tuning Fine grain program tuning]. We would like to fully test and sync these developments with mainline GCC within next month or two. | ||
| - | *'''2009.August.05''' - The colleagues from the [http://unidapt.org UNIDAPT Group] started investigating the use of [http://ctuning.org cTuning]/[http://cTuning.org/project-milepost MILEPOST] technology and the [http://ctuning.org/unidapt UNIDAPT framework] to predict good optimization and parallelization schemes for hybrid heterogeneous CPU/GPU-like architectures together with [http://www.caps-entreprise.com CAPS Entreprise] based on run-time adaptation and profiling, empirical iterative compilation, statistical analysis, machine learning, program and dataset features and run-time decision trees ({{Ref|FT2009}}, {{Ref|LCWP2009}}, {{Ref|Fur2009}}, {{Ref|JGVP2009}}, {{Ref1|TWFP2009}}, {{Ref|FMTP2008}}, {{Ref|LFF2007}}, {{Ref|FCOP2005}}). They plan to add new optimization cases to the [http://ctuning.org/cdatabase Collective Optimization Database] in Autumn, 2009. | + | *'''2009.August.05''' - The colleagues from the [http://unidapt.org UNIDAPT Group] started investigating the use of [http://ctuning.org cTuning]/[http://cTuning.org/project-milepost MILEPOST] technology and the [http://ctuning.org/unidapt UNIDAPT framework] to predict good optimization and parallelization schemes for hybrid heterogeneous CPU/GPU-like architectures together with [http://www.caps-entreprise.com CAPS Entreprise] based on run-time adaptation and profiling, empirical iterative compilation, statistical analysis, machine learning, program and dataset features and run-time decision trees ({{Ref|FT2010}}, {{Ref|FT2009}}, {{Ref|LCWP2009}}, {{Ref|Fur2009}}, {{Ref|JGVP2009}}, {{Ref1|TWFP2009}}, {{Ref|FMTP2008}}, {{Ref|LFF2007}}, {{Ref|FCOP2005}}). They plan to add new optimization cases to the [http://ctuning.org/cdatabase Collective Optimization Database] in Autumn, 2009. |
*'''2009.July.27''' - The paper "Portable Compiler Optimization Across Embedded Programs and Microarchitectures using Machine Learning" ({{Ref|DJBP2009}}) has been accepted for the [http://www.microarch.org/micro42 42nd IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO)]. The research has been led by the colleagues from the University of Edinburgh - congratulations! | *'''2009.July.27''' - The paper "Portable Compiler Optimization Across Embedded Programs and Microarchitectures using Machine Learning" ({{Ref|DJBP2009}}) has been accepted for the [http://www.microarch.org/micro42 42nd IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO)]. The research has been led by the colleagues from the University of Edinburgh - congratulations! | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
*'''2009.June.26''' - The pdf of the paper that describes Collective Tuning Infrastructure and cTuning concept (presented at the GCC Summit'09) will be available in a few weeks [http://unidapt.org/index.php/Dissemination#Fur2009 here]. | *'''2009.June.26''' - The pdf of the paper that describes Collective Tuning Infrastructure and cTuning concept (presented at the GCC Summit'09) will be available in a few weeks [http://unidapt.org/index.php/Dissemination#Fur2009 here]. | ||
| - | *'''2009.June.10''' - Extended version of the "Collective Optimization" paper ({{Ref|FT2009|}}) describing collective tuning concept has been accepted for ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization (TACO). | + | *'''2009.June.10''' - Extended version of the "Collective Optimization" paper ({{Ref|FT2010}}, {{Ref|FT2009|}}) describing collective tuning concept has been accepted for ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization (TACO). |
*'''2009.June.03-10''' - We gave several talks/demos/tutorials about cTuning at the [http://www.hipeac.net/industry_workshop7 HiPEAC Computing week] (Infineon, Munich, Germany) and [http://www.gccsummit.org/2009 GCC Summit] (Montreal, Canada). | *'''2009.June.03-10''' - We gave several talks/demos/tutorials about cTuning at the [http://www.hipeac.net/industry_workshop7 HiPEAC Computing week] (Infineon, Munich, Germany) and [http://www.gccsummit.org/2009 GCC Summit] (Montreal, Canada). | ||
* '''2009.June.01''' - After nearly 1 year of developments we released/updated all our open-source collaborative [[CTools|R&D tools]]: | * '''2009.June.01''' - After nearly 1 year of developments we released/updated all our open-source collaborative [[CTools|R&D tools]]: | ||
Revision as of 00:05, 31 December 2010
 |
Collective Optimization Database |
| Sharing and reusing optimization knowledge to help tuning computing systems collectively |
Web shortcut: http://cTuning.org/cdatabase cTuning.org - free, open source, collaborative repository and tools for program and architecture characterization and optimization. It may not always be visible to the IT users, but developing and optimizing current and emerging computing systems using available technology is too time consuming and costly. Therefore, Dr. Grigori Fursin created Collective Optimization Database to enable collaborative sharing of useful optimization cases with the community to help optimize available computing systems (ranging from supercomputers to embedded systems) and enable development of the emerging intelligent self-tuning adaptive computing systems based on collective optimization, run-time adaptation, statistical and machine learning techniques. Some more scientific aspects/details on Collective Optimization can be found in the following ACM TACO'10 publication. 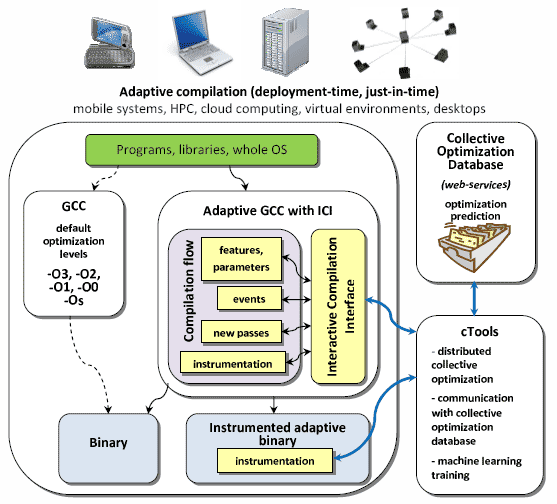 Collective Optimization Database (cDatabase or COD) provides a common global repository with data analysis plugins to share, analyze and reference useful program/architecture optimization cases. It has been developed to help users optimize programs, libraries, kernels and the whole systems (compiler optimizations/architecture configurations to improve execution time, code size, architecture size, power consumption, etc). It is intended to simplify and automate the design and optimization of programs, compilers, run-time systems and architectures based on recent statistical and machine learning techniques (FT2010, FT2009, FMTP2008, ABCP2006, MILEPOST, UNIDAPT). We also hope that it will also be useful for adaptive parallelization and scheduling for the emerging and future heterogeneous multi-core systems including current CPU/GPU and CELL architectures (LCWP2009). Finally, it is intended to improve the quality of academic research by avoiding costly duplicate experiments and providing replicable referable results. It can provide detailed performance analysis and comparison of different programs, datasets, compilers and architectures. It can be used to optimize programs on-the-fly when using cloud computing services. We currently keep information about architectures and their configurations, software environments, programs, datasets, compilers (such as GCC, Open64, ICC, PathScale and plan to add dynamic compilers such as LLVM, IBM Testerossa, etc), compiler flags for program and architecture optimizations, compiler ICI optimization passes, fine-grain program optimizations, execution time, code size, profiling statistics, program static and dynamic features (hardware counters), parallelization schemes, etc. cDatabase is an evolving project driven by the community and industry demands - you are welcome to join the project, extend the database and data analysis plugins, provide feedback and add your optimization data to help the community. If you want to use database directly, you can find more info about cDatabase API and web-services in cDatabase documentation. You can also communicate with cTuning community through our mailing lists. |
|







