From cTuning.org
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
{{CMenu:CTools|}} | {{CMenu:CTools|}} | ||
| - | <div style="color:red; font-weight:bold">MILEPOST GCC is now a part of the [[CTools:CTuningCC|cTuning Compiler Collection (cTuning CC)]].</div> | + | |
| + | <div style="color:red; font-weight:bold; "><H2>MILEPOST GCC is now a part of the [[CTools:CTuningCC|cTuning Compiler Collection (cTuning CC)]].</H2></div> | ||
| + | |||
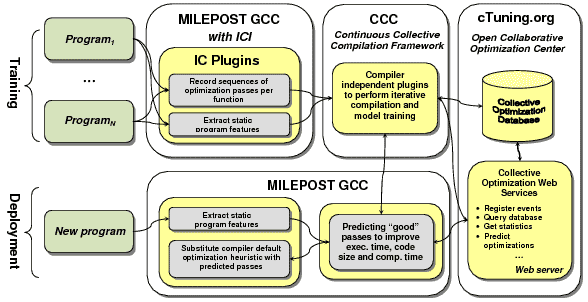
MILEPOST GCC is the first practical attept to build machine learning enabled open-source self-tuning production (and research) compiler that can adapt to any architecture using iterative feedback-directed compilation, machine learning and collective optimization. It is based on production quality [http://gcc.gnu.org GCC] that supports more than 30 families of architectures and can compile real, large applications including Linux, and on [[CTools:ICI|Interactive Compilation Interface]] that provides plugin system to access internals of compilers. MILEPOST GCC attempts to correlate [[CTools:MilepostGCC:StaticFeatures|program features]] and [[CDatabase|program optimizations]] during empirical iterative compilation to predict good optimizations for unseen programs based on prior learning. MILEPOST and cTuning infrastructure automates code and architecture optimization to improve execution time, code size, compilation time and other characteristics at the same time. This technology is not GCC-dependent and can be used in any compiler using common [[CTools:ICI|Interactive Compilation Interface]] and compiler independent plugins. The first version of the MILEPOST GCC and [[CTools:MilepostFramework|MILEPOST framework]] has been created during the [http://cTuning.org/project-milepost MILEPOST project]. All public MILEPOST developments have been coordinated by [http://fursin.net/research Grigori Fursin]. More information can be found in the following paper about [http://unidapt.org/index.php/Dissemination#FMTP2008 MILEPOST GCC]. | MILEPOST GCC is the first practical attept to build machine learning enabled open-source self-tuning production (and research) compiler that can adapt to any architecture using iterative feedback-directed compilation, machine learning and collective optimization. It is based on production quality [http://gcc.gnu.org GCC] that supports more than 30 families of architectures and can compile real, large applications including Linux, and on [[CTools:ICI|Interactive Compilation Interface]] that provides plugin system to access internals of compilers. MILEPOST GCC attempts to correlate [[CTools:MilepostGCC:StaticFeatures|program features]] and [[CDatabase|program optimizations]] during empirical iterative compilation to predict good optimizations for unseen programs based on prior learning. MILEPOST and cTuning infrastructure automates code and architecture optimization to improve execution time, code size, compilation time and other characteristics at the same time. This technology is not GCC-dependent and can be used in any compiler using common [[CTools:ICI|Interactive Compilation Interface]] and compiler independent plugins. The first version of the MILEPOST GCC and [[CTools:MilepostFramework|MILEPOST framework]] has been created during the [http://cTuning.org/project-milepost MILEPOST project]. All public MILEPOST developments have been coordinated by [http://fursin.net/research Grigori Fursin]. More information can be found in the following paper about [http://unidapt.org/index.php/Dissemination#FMTP2008 MILEPOST GCC]. | ||
Revision as of 19:39, 28 June 2010
 |
MILEPOST GCC |
| machine-learning enabled self-tuning compiler |
Web shortcut: http://cTuning.org/milepost-gcc Navigation: cTuning.org > CTools
MILEPOST GCC is now a part of the cTuning Compiler Collection (cTuning CC).
|
|