From cTuning.org
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <div style="font-style: italic;" > | |
| + | It may not always be visible to the IT users, but developing and optimizing current and emerging computing systems using available technology is excessively inefficient, time consuming and costly. During last several decades, many research papers have been published with suggestions about how to easily solve all these problems! Unfortunately, we often struggled replicating those results in realistic environments or finding stable practical tools based on these research papers. Therefore, we decided to create this collaborative Collective Tuning wiki-based portal to develop common practical open-source extensible collaborative infrastructure, benchmarks and collective optimization repository based on multiple research techniques and production tools to parametrize, automate and simplify program, compiler and architecture design and optimization using collective tuning, run-time adaptation, statistical and machine learning techniques. This technology minimizes repetitive time consuming tasks and human intervention: even though there is still a lot to be done, we are glad to see it helping several companies, end users and researchers to improve execution time, code size, power consumption, reliability and other important characteristics of the available computing systems ranging from supercomputers to mobile systems automatically. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
{|border="0" cellpadding="15" cellspacing="0" | {|border="0" cellpadding="15" cellspacing="0" | ||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
| - | We | + | We developed [http://cTuning.org/cdatabase Collective Optimization Database] to continuously collect a large number of optimization cases from the community to learn how to correlate program features, program and system behavior and good optimizations between multiple programs, datasets, compilers, operating systems and architectures. This repository is also intended to improve the quality of academic research by avoiding costly duplicate experiments and providing reproducible results. |
| - | + | ||
| - | '''''Note:''' cTuning is an ongoing evolving project - please be patient and tolerant to the community | + | cTuning infrastructure is still far from solving all optimization problems but we hope that it already opens up some interesting collaborative R&D opportunities to the community to develop intelligent self-tuning adaptive computing systems. We hope to gradually see more of this technology supported by multiple production compilers including GCC, LLVM, Rose, Open64, IBM and Intel compiler suites, and by multiple operating systems including Moblin, Android, standard desktop/server Linux distributions, Windows, cloud/distributed operating systems and so on. We would like to thank all [[Community:People|cTuning colleagues and users]] who are or have been helping with this project. |
| + | |||
| + | '''''Note:''' cTuning is an ongoing evolving project - please be patient and tolerant to the community. You are warmly welcome to [[Join|join cTuning community]] to help us parametrize and automate code, compiler and architecture design and optimization!'' | ||
'''Current design of our Collective Optimization Framework''': | '''Current design of our Collective Optimization Framework''': | ||
Revision as of 23:45, 14 March 2010
It may not always be visible to the IT users, but developing and optimizing current and emerging computing systems using available technology is excessively inefficient, time consuming and costly. During last several decades, many research papers have been published with suggestions about how to easily solve all these problems! Unfortunately, we often struggled replicating those results in realistic environments or finding stable practical tools based on these research papers. Therefore, we decided to create this collaborative Collective Tuning wiki-based portal to develop common practical open-source extensible collaborative infrastructure, benchmarks and collective optimization repository based on multiple research techniques and production tools to parametrize, automate and simplify program, compiler and architecture design and optimization using collective tuning, run-time adaptation, statistical and machine learning techniques. This technology minimizes repetitive time consuming tasks and human intervention: even though there is still a lot to be done, we are glad to see it helping several companies, end users and researchers to improve execution time, code size, power consumption, reliability and other important characteristics of the available computing systems ranging from supercomputers to mobile systems automatically.
|
We developed Collective Optimization Database to continuously collect a large number of optimization cases from the community to learn how to correlate program features, program and system behavior and good optimizations between multiple programs, datasets, compilers, operating systems and architectures. This repository is also intended to improve the quality of academic research by avoiding costly duplicate experiments and providing reproducible results. cTuning infrastructure is still far from solving all optimization problems but we hope that it already opens up some interesting collaborative R&D opportunities to the community to develop intelligent self-tuning adaptive computing systems. We hope to gradually see more of this technology supported by multiple production compilers including GCC, LLVM, Rose, Open64, IBM and Intel compiler suites, and by multiple operating systems including Moblin, Android, standard desktop/server Linux distributions, Windows, cloud/distributed operating systems and so on. We would like to thank all cTuning colleagues and users who are or have been helping with this project. Note: cTuning is an ongoing evolving project - please be patient and tolerant to the community. You are warmly welcome to join cTuning community to help us parametrize and automate code, compiler and architecture design and optimization! Current design of our Collective Optimization Framework: 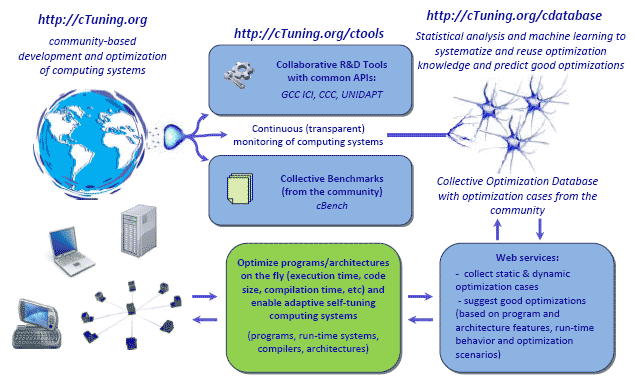 We are participating in the following collaborative activities:
Motivation example: Example of complex optimization search spaces for susan_c from Collective Benchmark after using CCC framework and MILEPOST GCC 4.4.0:  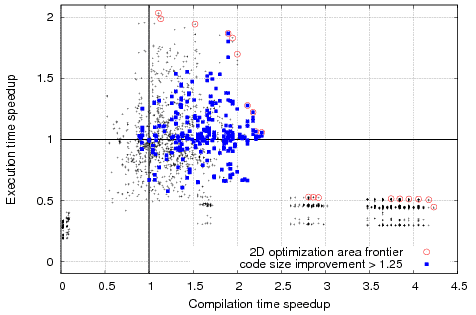 Example of program similarities based on static program features and based on best found program optimizations continuously collected in the cTuning optimization repository that improve execution time (though it can be any combination of execution time, code size, compilation time, etc):   Milepost GCC combined with cTuning technology helps to correlate program features and optimizations using various machine learning techniques to quickly predict good optimizations for a previously unseen program. |
|







