From cTuning.org
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Typical non-trivial distribution of optimization points in the 2D space of speedups vs code size of a ''susan_corners'' program on AMD Athlon64 3700+ architecture with GCC 4.4 during automatic program optimization using ''ccc-run-glob-flags-rnd-uniform'' plugin from [[CTools:CCC|CCC framework]] with uniform random combinations of more than 100 global compiler flags (each flag has 50% probability to be selected for a given combination of optimizations). Similar program optimization/characterization data for other benchmarks, datasets and architectures is collected continuously in the public [[CDatabase|Collective Optimization Database]].<BR> | Typical non-trivial distribution of optimization points in the 2D space of speedups vs code size of a ''susan_corners'' program on AMD Athlon64 3700+ architecture with GCC 4.4 during automatic program optimization using ''ccc-run-glob-flags-rnd-uniform'' plugin from [[CTools:CCC|CCC framework]] with uniform random combinations of more than 100 global compiler flags (each flag has 50% probability to be selected for a given combination of optimizations). Similar program optimization/characterization data for other benchmarks, datasets and architectures is collected continuously in the public [[CDatabase|Collective Optimization Database]].<BR> | ||
| - | <div align="center">http:// | + | <div align="center">http://cTuning.org/wiki/images/fig_opt_case_susan_c_1.gif http://cTuning.org/wiki/images/fig_opt_case_susan_c_2.gif</div> |
Example of program similarities based on [http://ctuning.org/wiki/index.php/CTools:MilepostGCC:StaticFeatures static program features] and based on best found program optimizations from the [http://cTuning.org/cdatabase cTuning optimization repository] that improve execution time: | Example of program similarities based on [http://ctuning.org/wiki/index.php/CTools:MilepostGCC:StaticFeatures static program features] and based on best found program optimizations from the [http://cTuning.org/cdatabase cTuning optimization repository] that improve execution time: | ||
| - | <div align="center">http:// | + | <div align="center">http://cTuning.org/wiki/images/img_influence_features.gif http://cTuning.org/wiki/images/img_influence_optimizations.gif</div>. |
[http://cTuning.org/milepost-gcc Milepost GCC] combined with cTuning technology helps to correlate program features and optimizations using various machine learning techniques to quickly predict good optimizations for a previously unseen program. | [http://cTuning.org/milepost-gcc Milepost GCC] combined with cTuning technology helps to correlate program features and optimizations using various machine learning techniques to quickly predict good optimizations for a previously unseen program. | ||
Revision as of 16:52, 10 March 2010
It may not always be visible to the IT users, but developing and optimizing current and emerging computing systems using available technology is too time consuming and costly. cTuning.org is an open community-driven collaborative wiki-based portal that brings together academia, industry and end-users to develop intelligent collective tuning technology that automates and simplifies compiler, program and architecture design and optimization. This technology minimizes repetitive time consuming tasks and human intervention using collective optimization, run-time adaptation, statistical and machine learning techniques. It can already help end users and researchers to improve execution time, code size, power consumption, reliability and other important characteristics of the available computing systems automatically (ranging from supercomputers to embedded systems) and should eventually enable development of the emerging intelligent self-tuning adaptive computing systems. Collective Optimization Database is intended to improve the quality of academic research by avoiding costly duplicate experiments and providing reproducible results.
|
We are very grateful to all our colleagues and users for providing valuable feedback or contributing to the project. You are warmly welcome to join this community-driven collaborative effort to help automate code, compiler and architecture design and optimization, boost innovation and research. Note: cTuning is an ongoing evolving project - please be patient and tolerant to the community and help us with this collaborative effort! 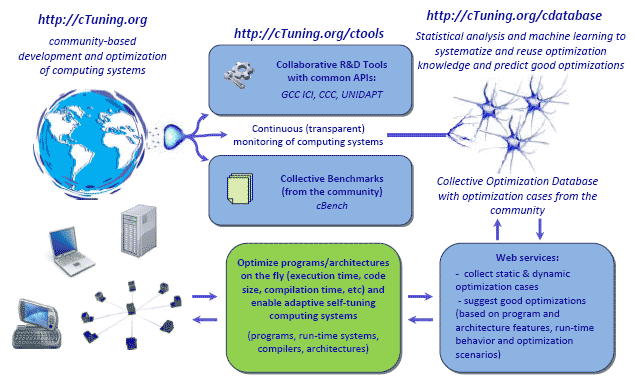 Typical non-trivial distribution of optimization points in the 2D space of speedups vs code size of a susan_corners program on AMD Athlon64 3700+ architecture with GCC 4.4 during automatic program optimization using ccc-run-glob-flags-rnd-uniform plugin from CCC framework with uniform random combinations of more than 100 global compiler flags (each flag has 50% probability to be selected for a given combination of optimizations). Similar program optimization/characterization data for other benchmarks, datasets and architectures is collected continuously in the public Collective Optimization Database.   Example of program similarities based on static program features and based on best found program optimizations from the cTuning optimization repository that improve execution time:   Milepost GCC combined with cTuning technology helps to correlate program features and optimizations using various machine learning techniques to quickly predict good optimizations for a previously unseen program. We are participating in the following collaborative activities:
|
|







