From cTuning.org
Current revision (15:51, 12 September 2015) (view source) |
|||
| (97 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | '''''NEWS: Since 2015, we moved all related developments to our new [http://github.com/ctuning/ck/wiki Collective Knowledge Framework]! Demo of a new live repository is available [http://cknowledge.org/repo here].''''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{CTitle|http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/milepost_image.jpg|MILEPOST GCC|machine-learning enabled self-tuning compiler}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{CShortCut|milepost-gcc}} | ||
| + | |||
{{CMenu:CTools|}} | {{CMenu:CTools|}} | ||
| - | + | {{NEWS}} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | * | + | <div style="color:red; font-weight:bold; "><H2> |
| - | * ' | + | * MILEPOST GCC is now a part of the [[CTools:CTuningCC|cTuning Compiler Collection (cTuning CC)]]. |
| + | * Reference publication about MILEPOST GCC in IJPP'11 is now available [http://fursin.net/wiki/index.php5?title=Research:Dissemination#FKMP2011 here]. | ||
| + | </H2></div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | MILEPOST GCC is the first practical attept to build machine learning enabled open-source self-tuning production (and research) compiler that can adapt to any architecture using iterative feedback-directed compilation, machine learning and collective optimization. It is based on production quality [http://gcc.gnu.org GCC] that supports more than 30 families of architectures and can compile real, large applications including Linux, and on [[CTools:ICI|Interactive Compilation Interface]] that provides plugin system to access internals of compilers. MILEPOST GCC attempts to correlate [[CTools:MilepostGCC:StaticFeatures|program features]] and [[CDatabase|program optimizations]] during empirical iterative compilation to predict good optimizations for unseen programs based on prior learning. MILEPOST and cTuning infrastructure automates code and architecture optimization to improve execution time, code size, compilation time and other characteristics at the same time. This technology is not GCC-dependent and can be used in any compiler using common [[CTools:ICI|Interactive Compilation Interface]] and compiler independent plugins. The first version of the MILEPOST GCC and [[CTools:MilepostFramework|MILEPOST framework]] has been created during the [http://cTuning.org/project-milepost MILEPOST project]. All public MILEPOST developments have been coordinated by [http://fursin.net/research Grigori Fursin]. More information can be found in the following paper about [http://unidapt.org/index.php/Dissemination#FMTP2008 MILEPOST GCC]. | |
| - | + | <div align="center">http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/img-milepost-gcc-structure.gif</div> | |
| - | + | * '''Background:''' | |
| - | * [ | + | **[[CTools:MilepostGCC:Motivation|Motivation and history]] |
| - | * [ | + | **[[CTools:MilepostGCC:Usage|Usage scenarios / stories]] |
| - | * [ | + | **[[CTools:MilepostGCC:Resources|Resources (links, publications, etc)]] |
| - | + | * [[CTools:MilepostGCC:Downloads|'''Downloads''']] | |
| + | |||
| + | * [[CTools:MilepostGCC:Documentation|'''Documentation''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[CTools:MilepostGCC:Feedback|'''User suggestions and feedback''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[CTools:MilepostGCC:Dev:Bugs|'''Bug reports''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[CTools:MilepostGCC:FAQs|'''FAQs''']] - Does MILEPOST GCC solve all optimization problems? How similar is it ACOVEA tool? etc... | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Related:''' | ||
| + | ** [http://ctuning.org/wiki/index.php/Special:CPredict Online predictor of optimizations based on program features]. | ||
| + | ** [[CDatabase|Collective optimization repository]] to continuously collect profitable optimization cases from the community that improve program execution time, code size, compilation time, etc... | ||
| + | ** [[CTools:CCC|CCC framework]] - Continuous Collective Compilation Framework to automate search of profitable optimization cases to improve program execution time, code size, compilation time, etc. It is used to train MILEPOST GCC and has some similarities with the useful [http://www.coyotegulch.com/products/acovea ACOVEA tool] but also allows automatic sharing of optimization knowledge with the community in the [[CDatabase|Collective Optimization Database]] and uses plugins to implement various search techniques besides genetic algorithms. | ||
| + | ** [http://cTuning.org/project-milepost Official info for the MILEPOST project (2006-2009)]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div align="center"> | ||
| + | {| cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" border="0" width="100%" style="color: black;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background: rgb(0, 100, 159) none repeat scroll 0% 0%; -moz-background-clip: -moz-initial; -moz-background-origin: -moz-initial; -moz-background-inline-policy: -moz-initial; color: white;" | '''MILEPOST GCC friends:''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" valign="top" | {{CTools:MilepostGCC:Logo_Friends}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
Current revision
NEWS: Since 2015, we moved all related developments to our new Collective Knowledge Framework! Demo of a new live repository is available here.
 |
MILEPOST GCC |
| machine-learning enabled self-tuning compiler |
Web shortcut: http://cTuning.org/milepost-gcc
Navigation: cTuning.org > CTools
NOTES:
- Reference publications about cTuning.org long-term vision: GCC Summit'09, ACM TACO'10 journal and IJPP'11 journal.
- MILEPOST GCC is now a part of the cTuning Compiler Collection (cTuning CC).
- Reference publication about MILEPOST GCC in IJPP'11 is now available here.
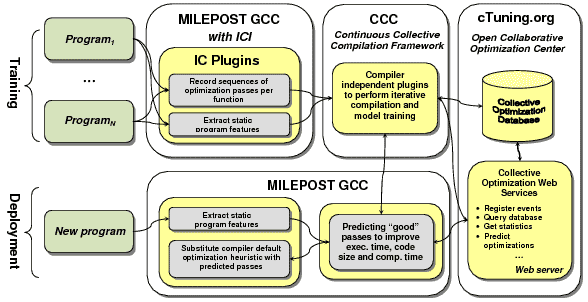
MILEPOST GCC is the first practical attept to build machine learning enabled open-source self-tuning production (and research) compiler that can adapt to any architecture using iterative feedback-directed compilation, machine learning and collective optimization. It is based on production quality GCC that supports more than 30 families of architectures and can compile real, large applications including Linux, and on Interactive Compilation Interface that provides plugin system to access internals of compilers. MILEPOST GCC attempts to correlate program features and program optimizations during empirical iterative compilation to predict good optimizations for unseen programs based on prior learning. MILEPOST and cTuning infrastructure automates code and architecture optimization to improve execution time, code size, compilation time and other characteristics at the same time. This technology is not GCC-dependent and can be used in any compiler using common Interactive Compilation Interface and compiler independent plugins. The first version of the MILEPOST GCC and MILEPOST framework has been created during the MILEPOST project. All public MILEPOST developments have been coordinated by Grigori Fursin. More information can be found in the following paper about MILEPOST GCC.
- FAQs - Does MILEPOST GCC solve all optimization problems? How similar is it ACOVEA tool? etc...
- Related:
- Online predictor of optimizations based on program features.
- Collective optimization repository to continuously collect profitable optimization cases from the community that improve program execution time, code size, compilation time, etc...
- CCC framework - Continuous Collective Compilation Framework to automate search of profitable optimization cases to improve program execution time, code size, compilation time, etc. It is used to train MILEPOST GCC and has some similarities with the useful ACOVEA tool but also allows automatic sharing of optimization knowledge with the community in the Collective Optimization Database and uses plugins to implement various search techniques besides genetic algorithms.
- Official info for the MILEPOST project (2006-2009).