From cTuning.org
Navigation: cTuning.org > CTools
- Download MILEPOST GCC 4.4.0
- Access online optimization predictor based on program features
- Access collective optimization repository
- Further developments (within GCC ICI)
- Google Summer of Code'09 MILEPOST GCC extensions and plugins (XML representation of the compilation flow, fine-grain optimizations and instrumentation, polyhedral transformations, run-time adaptation)
- cTuning development mailing list
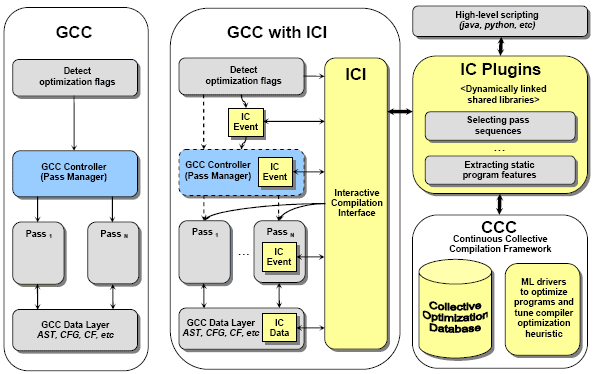
MILEPOST GCC is the first machine learning enabled open-source self-tuning research compiler that can adapt to any architecture using iterative feedback-directed compilation, machine learning and collective optimization. It combines the strength of the production quality GCC that supports more than 30 families of architectures and can compile real, large applications including Linux, and the flexibility of the Interactive Compilation Interface that transforms GCC into the research compiler. It is currently based on predictive modeling using program and machine-specific features, execution time, hardware counters and offline training. MILEPOST GCC includes IBM static program feature extractor.
The development of the MILEPOST GCC and MILEPOST Framework has been coordinated by Dr. Grigori Fursin (2006-2009) and the UNIDAPT group within EU FP6 MILEPOST project (the project consortium includes INRIA, France; the IBM Haifa Research Lab, Israel; the University of Edinburgh, UK; ARC International Ltd., UK; CAPS Enterprise, France) with the help of Cupertino Miranda and Zbigniew Chamski (extending Interactive Compilation Interface), Edwin Bonilla (extending machine learning techniques), Mircea Namolaru (integrating static program feature extractor) and John Thomson (performance evaluation).
In June, 2009, MILEPOST GCC has been released and all further developments have been integrated with the cTuning tools: Collective Optimization Database, cTuning optimization prediction web-services, Interactive Compilation Interface for GCC, Continuous Collective Compilation Framework to enable collaborative community-driven developments after the end of the MILEPOST project (August 2009). You are warmly welcome to join cTuning community and follow/participate in developments and discussions using cTuning Wiki-based portal and 2 mailing lists: high volume development list and low volume announcement list. It is an on-going long term project, so next we would like to try to test MILEPOST GCC/cTuning framework to optimize whole Linux (Gentoo-like), optimize programs for mobile systems on the fly (Android, Moblin, etc) and extend this technology to enable realistic adaptive parallelization, data partitioning and scheduling for heterogeneous multi-core systems using statistical and machine learning techniques.
More details about our current and future developments can be found in the following publications:
- "MILEPOST GCC: machine learning based research compiler"
- "Collective Optimization"
- "Collective Tuning Initiative: automating and accelerating development and optimization of computing systems"
Brief motivation: Tuning hardwired compiler optimizations for rapidly evolving hardware makes porting an optimizing compiler for each new platform extremely challenging. Our radical approach is to develop a modular, extensible, self-tuning intelligent compiler that automatically learns the best optimization heuristics based on combining feedback-directed iterative compilation and machine learning. MILEPOST GCC is a machine learning based compiler that automatically adjusts its optimization heuristics to improve execution time, code size, or compilation time of specific programs on different architectures. Currently, we use several iterative search strategies within CCC framework to find combinations of good optimization flags to substitute GCC default optimization levels for a particular architecture (such as -O0,-O1,-O2,-O3,-Os which we will not need in the future adaptive compilers) or tune optimization passes on a function-level for a particular program. Our preliminary experimental results (some are available in [Collective Optimization Database) show that it is possible to considerably reduce execution time and code size of various benchmarks (MiBench, MediaBench, EEMBC, SPEC) on a range of platforms (x86, x8664, IA64, ARC, Loongson/Godson, etc) entirely automatically. MILEPOST GCC can be used interactively in research on adaptive computing through the Interactive Compilation Interface (we currently support optimization pass selection and reordering, plugins and event mechanism to invoke any passes on demand (such as program feature extraction pass) or tune cost-models of specific transformations within passes). CCC framework provides a milepost-gcc wrapper that detects -ml flag, extracts program features, queries optimization prediction web-service connected to optimization repository and substitutes default optimizations with the suggested ones based on program similarities and machine learning to improve execution time or code size on the fly.