|
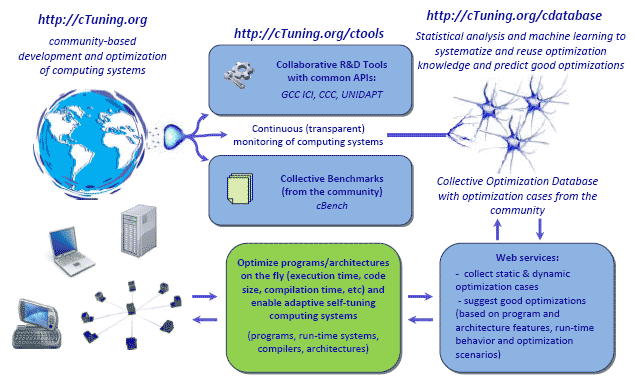
It may not always be visible to the IT users, but developing and optimizing current and emerging computing systems using available technology is too time consuming and costly. cTuning.org is a community-driven collaborative wiki-based project that brings together academia, industry and end-users to develop intelligent collective tuning technology that automates and simplifies compiler, program and architecture design and optimization. This technology minimizes repetitive time consuming tasks and human intervention using collective optimization, run-time adaptation, statistical and machine learning techniques. It can already help to improve performance, power consumption, reliability and other important characteristics of the available computing systems automatically (ranging from supercomputers to embedded systems) and should eventually enable development of the emerging intelligent self-tuning adaptive computing systems.
We are participating in the following collaborative activities:
- Develop common open-source tools with unified APIs (universal compilers adaptable to any heterogeneous multi-core architecture, computer architecture simulators, adaptive run-time systems) to optimize programs and architectures collectively using iterative compilation, statistical and machine learning techniques.
- Share interesting optimization cases from the community for programs/libraries/OS (compiler optimizations/architecture configurations to improve execution time, code size, architecture size, power consumption, etc) in the Collective Optimization Database to help users optimize their systems, enable replicable collaborative research and enable further analysis using statistical and machine learning techniques.
- Enable collaborative research using cTools to automate and simplify the process of developing and optimizing new computer architectures, compilers, operating systems and programming environments using statistical analysis, machine learning, dynamic adaptation and bio-inspired techniques. We believe that our adaptive approaches are critical to overcome the complexity of computing systems and improve their performance, power consumption, system size and fault-tolerance automatically while reducing their cost and time to market.
Everyone is welcome to use cTools for their R&D, browse and update cDatabase, provide feedback or join cTuning initiative to actively participate in this collaborative effort, extend cTools, cResearch and propose your new collaborative R&D projects for the cTuning community. We hope that this community effort will boost innovation in compiler, OS and architecture technology, provide novel adaptive mechanisms for heterogeneous, reconfigurable multi-core systems and emerging technologies such as cloud computing, will simplify program and architecture design and optimization, reduce system cost and and will eventually have a positive effect on science and industries that demand ever-increasing computing resources while placing strict requirements on systems.
You can find more information about our motivation and the history of this project at our Mission page.
General cTuning R&D directions are modestly moderated by our steering committee.
You can contact cTuning admins directly if you have general questions.
Note: cTuning is an ongoing evolving project - please be patient and tolerant to the community and help us with this collaborative effort!
|
| News
|
- 2009.June.26 - We participated in discussions to include plugin system similar to ICI to mainline GCC for a long time and finally GCC 4.5 will feature a low-level plugin system. We are now synchronizing high-level ICI/MILEPOST with the mainline to be able to reuse all our available plugins. We also develop several new plugins within Google Summer of Code'2009 to enable XML representation of the compilation flow, fine-grain program optimizations and instrumentation, automatic tuning of optimization heuristic based on machine learning, and function-level run-time adaptation. Comparison of GCC low-level and high-level ICI plugins is available here. The ICI development and discussions mailing list is available here.
- 2009.June.10 - Extended version of the "Collective Optimization" paper (FT2009) describing collective tuning concept has been accepted for ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization (TACO).
- 2009.June.03-10 - We gave several talks/demos/tutorials about cTuning at the HiPEAC Computing week (Infineon, Munich, Germany) and GCC Summit (Montreal, Canada).
- 2009.June.01 - After nearly 1 year of developments we released/updated all our open-source collaborative R&D tools:
- fully redesigned and documented Interactive Compilation Interface v2.0 for GCC 4.4.0 synchronized with the official plugin GCC branch - transforming compilers into plugin-enabled research toolsets
- MILEPOST GCC 4.4.0 pre-release version at SVN - automating program optimization and compiler optimization heuristic tuning using machine learning
- Continuous Collective Compilation Framework v2.0 - enabling automatic collaborative program optimization based on statistical and machine learning techniques
- Collective Benchmark/MiDataSets v1.0 - enabling realistic program optimization research and benchmarking using multiple open-source programs/datasets.
We also updated Collective Optimization Database with various optimization cases for Intel and AMD processors and comparison of different compilers including GCC, LLVM, Open64, Intel, etc - enabling sharing and reuse of optimization knowledge.
We would like to thank cTuning community for feedback, help and support! You are welcome to join this community effort to automate program optimization and compiler/architecture design.
- 2009.April.27 - We gave a talk at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign about Collective Tuning Initiative and tools and MILEPOST project ("Collective Optimization, run-time adaptation and machine learning"). Presentation is available here. We would like to thank all the UIUC colleagues for a very interesting and useful feedback.
- 2009.April.23 - Preview version of the optimization predictor based on static program features and machine learning (to improve program execution time, code size, etc) is now available on-line. It is an on-going project, so please be patient. Comments are welcome!
|
|