From cTuning.org
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
{{CMenu:CTools|}} | {{CMenu:CTools|}} | ||
| - | ::::::::::: | + | <div style="font-style: italic; background-color: #FF7F7F"> |
| + | :::::::::''ANNOUNCEMENT:'' After the release of the [[CTools:CTuningCC|cTuning CC (MILEPOST GCC)]] and a relatively quiet summer and autumn 2010 spent mostly on thinking ;), we plan to resume our open collaborative activities in 2011 and will work on a new collaborative platform and a repository cTuning<sub>2</sub>. Currently, we are looking for additional funding to keep it running and to access various new hardware (embedded or HPC systems, GPUs, etc) to perform empirical collective learning and optimization to suggest better program optimizations or hardware designs based on multi-objective criteria (execution time/power/architecture size/code size/compilation time/etc) ([http://fursin.net/wiki/index.php5?title=Research:Dissemination#Fur2009 ref<sub>1</sub>], [http://fursin.net/wiki/index.php5?title=Research:Dissemination#FT2009 ref<sub>2</sub>], [[CDatabase|ref<sub>3</sub>]]), so if you are interested to support cTuning initiative in 2011, please don't hesitate to contact [http://fursin.net/research Dr. Grigori Fursin] (cTuning founder and R&D coordinator). More information will be available at the beginning of 2011.</div> | ||
cTuning CC is a free, open source compiler collection that combines multiple tools and techniques including [[CTools:MilepostGCC|MILEPOST GCC]], [[CTools:ICI|ICI]], [[CTools:CCC|CCC framework]], [[CDatabase|cTuning web-services and Collective Optimization Database]] and [[CTools:CBench|cBench]] as the first practical step toward self-tuning, adaptive computing systems based on industrial tools, empirical techniques, transparent collective optimization, statistical analysis and machine learning. cTuning CC is a wrapper around any compiler such as [http://gcc.gnu.org GCC], [http://llvm.org LLVM], [http://www.open64.net Open64], [http://www.pathscale.com Path64], etc that can transparently invoke machine learning mode to correlate program features of a compiled program with the ones stored in the [http://cTuning.org/cdatabase Collective Optimization Database] and suggest better optimizations for multi-objective criteria such as improving execution time, compilation time, code size, etc (using optimization space frontier detection). | cTuning CC is a free, open source compiler collection that combines multiple tools and techniques including [[CTools:MilepostGCC|MILEPOST GCC]], [[CTools:ICI|ICI]], [[CTools:CCC|CCC framework]], [[CDatabase|cTuning web-services and Collective Optimization Database]] and [[CTools:CBench|cBench]] as the first practical step toward self-tuning, adaptive computing systems based on industrial tools, empirical techniques, transparent collective optimization, statistical analysis and machine learning. cTuning CC is a wrapper around any compiler such as [http://gcc.gnu.org GCC], [http://llvm.org LLVM], [http://www.open64.net Open64], [http://www.pathscale.com Path64], etc that can transparently invoke machine learning mode to correlate program features of a compiled program with the ones stored in the [http://cTuning.org/cdatabase Collective Optimization Database] and suggest better optimizations for multi-objective criteria such as improving execution time, compilation time, code size, etc (using optimization space frontier detection). | ||
Revision as of 21:34, 24 October 2010
 |
cTuning Compiler Collection |
| machine-learning enabled, self-tuning, adaptive compilers |
Web shortcut: http://cTuning.org/ctuning-cc Navigation: cTuning.org > CTools
cTuning CC is a free, open source compiler collection that combines multiple tools and techniques including MILEPOST GCC, ICI, CCC framework, cTuning web-services and Collective Optimization Database and cBench as the first practical step toward self-tuning, adaptive computing systems based on industrial tools, empirical techniques, transparent collective optimization, statistical analysis and machine learning. cTuning CC is a wrapper around any compiler such as GCC, LLVM, Open64, Path64, etc that can transparently invoke machine learning mode to correlate program features of a compiled program with the ones stored in the Collective Optimization Database and suggest better optimizations for multi-objective criteria such as improving execution time, compilation time, code size, etc (using optimization space frontier detection). It may not always be visible to the IT users, but developing and optimizing computing systems using available over-complicated technology is too time consuming and costly often resulting in underperforming, power-hungry and inefficient computers and programs. Novel cTuning technology attempts to overcome the complexity of computing system by automating architecture, code and dataset analysis, characterization and multi- objective optimization (currently execution time, code size and compilation time) and enabling portable optimization using
cTuning CC includes:
We are developing cTuning infrastructure as a very simple, modular and portable tool so that users could easily download, install and use it to compile, execute, characterize and optimize their programs or share optimization knowledge. Our users managed to optimize some large industrial applications such as BerkeleyDB (1.4 speedup over GCC 4.4.0 -O3 on several Intel Xeon machines), some audio and video codecs, multiple standard benchmarks, Linux kernel, etc. Please, note that this is an on-going, evolving project driven by the cTuning community, so please be patient or join the project and help to improve cTuning infrastructure. 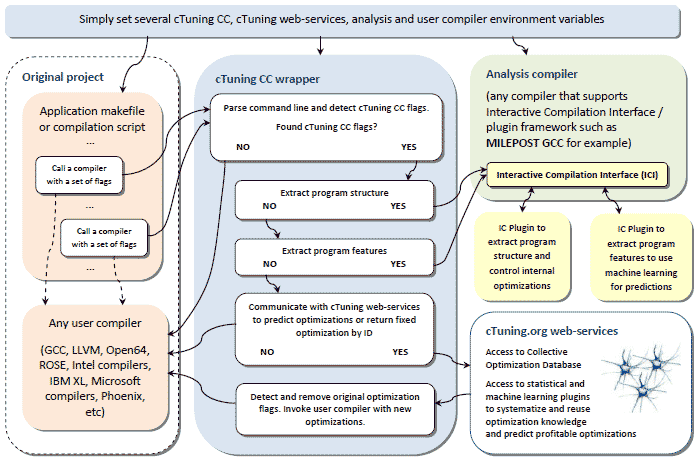 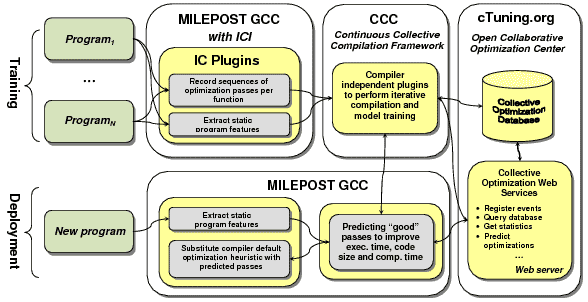
Example of complex optimization search spaces for susan_c (including optimization space frontier for multi-objective optimizations) from Collective Benchmark after using CCC framework (that has some similarities with the useful ACOVEA tool but also allows automatic sharing of optimization knowledge with the community in the Collective Optimization Database and uses plugins to implement various search techniques besides genetic algorithms) and cTuning CC/MILEPOST GCC 4.4.x:  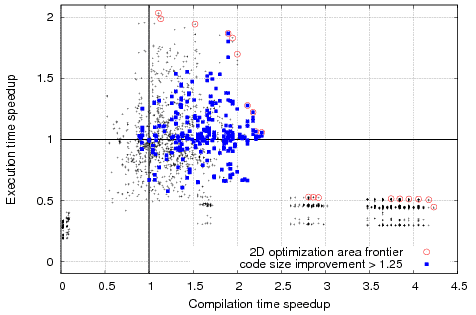 Example of program similarities using static program features and based on best found program optimizations continuously collected in the cTuning optimization repository that improve execution time (as well as code size, compilation time, etc):   cTuning CC/MILEPOST GCC 4.4.x helps to correlate program features and optimizations using various machine learning techniques to quickly predict good optimizations for a previously unseen program.
|
|






