From cTuning.org
Current revision (16:23, 17 February 2019) (view source) |
|||
| (193 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | '''''We moved all developments to our new [http://cKnowledge.org Collective Knowledge Framework] in 2015!''''' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <div | + | {{Reference}} |
| + | <div style="font-style: italic;" > | ||
| + | It may not be always visible to the end-users, but developing and optimizing emerging computer systems using current methodology and tools is excessively inefficient, time consuming and costly. During past decades, many research papers have been published about how to design and optimize computer systems. However, most of the time, we struggle to reproduce their results in realistic environments, or to find common open-source tools based on these research papers. Therefore, we created this collaborative tuning center with a public optimization repository to share data about behavior of computer systems, share free open-source code, benchmarks, data sets, and models from these tools, and let the community improve predictive models that correlate behavior of computer systems with various properties and characteristics of computer systems. cTuning technology is used to help academia and industry to collaboratively improve execution time, code size, power consumption, reliability and other important characteristics of emerging computer systems from HPC to mobile devices. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| - | cTuning | + | <div style="color:red; font-weight:bold">cTuning web-site and infrastructure is totally free and maintained by end-users (basically by you). It is an on-going project, so please be patient or join the effort by sharing optimization data, extending tools, exchanging ideas, referencing this work, etc. We created cTuning.org because we believe in the power of collaborative and open R&D, and because we would like to change sad trends in academic research where a number of published papers is often more important than usefulness, reproducibility and reusability of results including code, data and models!</div> |
| - | + | '''Current design of our Collective Optimization Framework''': | |
| - | + | <div align="center">http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/ctuning.gif</div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | We developed [http://cTuning.org/cdatabase Collective Optimization Database] to continuously collect a large number of optimization cases from the community to learn how to correlate program features, program and system behavior and good optimizations between multiple programs, datasets, compilers, operating systems and architectures. This repository is also intended to improve the quality of academic research by avoiding costly duplicate experiments and providing reproducible results. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | cTuning open-source infrastructure is still far from solving all optimization problems but we hope that it already opens up some interesting collaborative R&D opportunities to the community to develop intelligent self-tuning adaptive computing systems. We hope that cTuning-like technology will one day eventually improve production compilers that we use including [http://gcc.gnu.org GCC], [http://llvm.org LLVM], [http://rosecompiler.org Rose source-to-source tool], [http://www.open64.net Open64], IBM [http://www-01.ibm.com/software/awdtools/fortran XL] and [http://j9tr.blogspot.com Testarossa], [http://www.caps-entreprise.com/fr/page/index.php?id=49&p_p=36 HMPP directive based compiler for hybrid multicore systems], [http://software.intel.com/en-us/intel-compilers Intel] compiler suites, and operating systems including [http://moblin.org Moblin], [http://www.android.com Android], standard desktop/server Linux distributions, [http://www.microsoft.com/WINDOWS Windows], cloud/distributed operating systems and so on. We would like to thank all [[Community:People|cTuning colleagues and users]] who have been helping with this project. | |
| - | + | '''''Note:''' cTuning is an ongoing evolving project - please be patient and tolerant to the community. You are warmly welcome to [[Join|join cTuning community]] to help us parametrize and automate code, compiler and architecture design and optimization!'' | |
| - | <div align=" | + | |
| - | + | '''We have been participating in the following collaborative activities since 2006:''' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | * Develop common open-source tools with unified APIs (universal compilers adaptable to any heterogeneous multi-core architecture, computer architecture simulators, adaptive run-time systems) to optimize programs and architectures collectively using iterative compilation, statistical and machine learning techniques. <div align="right">''More information is available at [[CTools|cTools page]].''</div> | |
| - | + | * Share interesting optimization cases from the community for programs/libraries/OS (compiler optimizations/architecture configurations to improve execution time, code size, architecture size, power consumption, etc) in the Collective Optimization Database to help users optimize their systems, enable replicable collaborative research and enable further analysis using statistical and machine learning techniques.<br><div align="right">''More information is available at [[CDatabase|cDatabase page]].''</div> | |
| - | + | * Enable collaborative research using cTools to automate and simplify the process of developing and optimizing new computer architectures, compilers, operating systems and programming environments using statistical analysis, machine learning, dynamic adaptation and bio-inspired techniques. We believe that our adaptive approaches are critical to overcome the complexity of computing systems and improve their performance, power consumption, system size and fault-tolerance automatically while reducing their cost and time to market. <br><div align="right">''More information is available at [[CResearch|cResearch page]].''</div> | |
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | '''Motivation example:''' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | | | + | Example of complex optimization search spaces for susan_c (including optimization space frontier for multi-objective optimizations) from [[CTools:CBench|Collective Benchmark]] after using [[CTools:CCC|CCC framework]] (that has some similarities with the useful [http://www.coyotegulch.com/products/acovea ACOVEA tool] but also allows automatic sharing of optimization knowledge with the community in the [[CDatabase|Collective Optimization Database]] and uses plugins to implement various search techniques besides genetic algorithms) and [[CTools:CTuningCC|cTuning CC]]/[[CTools:MilepostGCC|MILEPOST GCC 4.4.x]]: |
| - | <div align="center">< | + | <div align="center">http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/fig_opt_case_susan_c_1.gif http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/fig_opt_case_susan_c_2.gif</div> |
| - | | | + | |
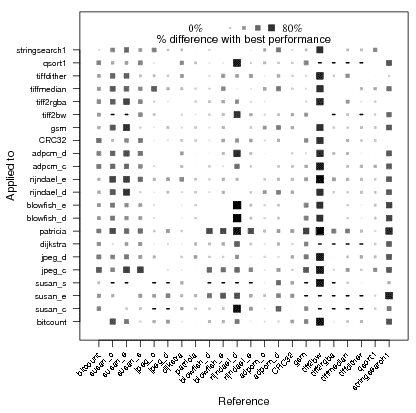
| - | < | + | Example of program similarities using [[CTools:MilepostGCC:StaticFeatures|static program features]] and based on best found program optimizations continuously collected in the [[CDatabase|cTuning optimization repository]] that improve execution time (as well as code size, compilation time, etc): |
| + | <div align="center">http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/img_influence_features.gif http://ctuning.org/wiki/images/img_influence_optimizations.gif</div>. | ||
| + | [[CTools:CTuningCC|cTuning CC]]/[[CTools:MilepostGCC|MILEPOST GCC]] uses online machine learning and prediction plugins to correlate program features and optimizations on the fly and quickly predict profitable optimizations for a previously unseen program and for multiple user objectives (balancing execution time, code size, compilation time, etc). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[CMind|Collective Mind]] framework and repository is the latest development by [http://cTuning.org/lab/people/gfursin Grigori Fursin] that aggregates all his past R&D to deliver new universal plugin-based framework to systematize and automate computer engineering using crowdsourcing and machine learning. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | cTuning foundation (non-profit association run by the community) is the outcome of the [http://ctuning.org/project-milepost EU FP6 MILEPOST project (2006-2009)]! | ||
Current revision
We moved all developments to our new Collective Knowledge Framework in 2015!
cTuning.org is based on the following reference publications: GCC Summit'09, CPE'04, HiPEAC'05, PhD thesis'04, SMART'09, PLDI'10, HiPEAC'09, IJPP'11
It may not be always visible to the end-users, but developing and optimizing emerging computer systems using current methodology and tools is excessively inefficient, time consuming and costly. During past decades, many research papers have been published about how to design and optimize computer systems. However, most of the time, we struggle to reproduce their results in realistic environments, or to find common open-source tools based on these research papers. Therefore, we created this collaborative tuning center with a public optimization repository to share data about behavior of computer systems, share free open-source code, benchmarks, data sets, and models from these tools, and let the community improve predictive models that correlate behavior of computer systems with various properties and characteristics of computer systems. cTuning technology is used to help academia and industry to collaboratively improve execution time, code size, power consumption, reliability and other important characteristics of emerging computer systems from HPC to mobile devices.
Current design of our Collective Optimization Framework:
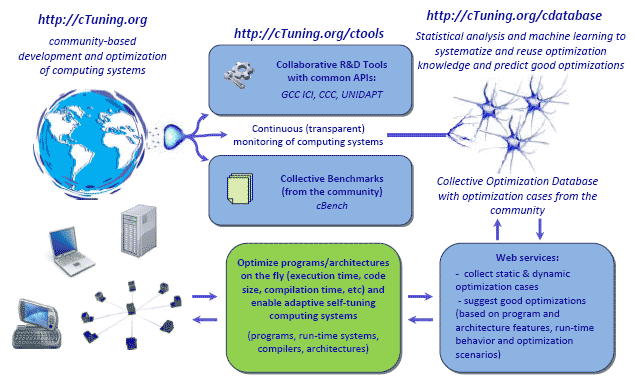
We developed Collective Optimization Database to continuously collect a large number of optimization cases from the community to learn how to correlate program features, program and system behavior and good optimizations between multiple programs, datasets, compilers, operating systems and architectures. This repository is also intended to improve the quality of academic research by avoiding costly duplicate experiments and providing reproducible results.
cTuning open-source infrastructure is still far from solving all optimization problems but we hope that it already opens up some interesting collaborative R&D opportunities to the community to develop intelligent self-tuning adaptive computing systems. We hope that cTuning-like technology will one day eventually improve production compilers that we use including GCC, LLVM, Rose source-to-source tool, Open64, IBM XL and Testarossa, HMPP directive based compiler for hybrid multicore systems, Intel compiler suites, and operating systems including Moblin, Android, standard desktop/server Linux distributions, Windows, cloud/distributed operating systems and so on. We would like to thank all cTuning colleagues and users who have been helping with this project.
Note: cTuning is an ongoing evolving project - please be patient and tolerant to the community. You are warmly welcome to join cTuning community to help us parametrize and automate code, compiler and architecture design and optimization!
We have been participating in the following collaborative activities since 2006:
- Develop common open-source tools with unified APIs (universal compilers adaptable to any heterogeneous multi-core architecture, computer architecture simulators, adaptive run-time systems) to optimize programs and architectures collectively using iterative compilation, statistical and machine learning techniques. More information is available at cTools page.
- Share interesting optimization cases from the community for programs/libraries/OS (compiler optimizations/architecture configurations to improve execution time, code size, architecture size, power consumption, etc) in the Collective Optimization Database to help users optimize their systems, enable replicable collaborative research and enable further analysis using statistical and machine learning techniques.More information is available at cDatabase page.
- Enable collaborative research using cTools to automate and simplify the process of developing and optimizing new computer architectures, compilers, operating systems and programming environments using statistical analysis, machine learning, dynamic adaptation and bio-inspired techniques. We believe that our adaptive approaches are critical to overcome the complexity of computing systems and improve their performance, power consumption, system size and fault-tolerance automatically while reducing their cost and time to market. More information is available at cResearch page.
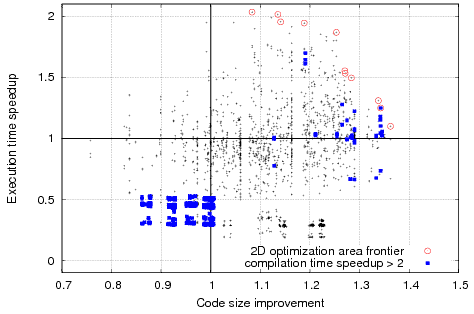
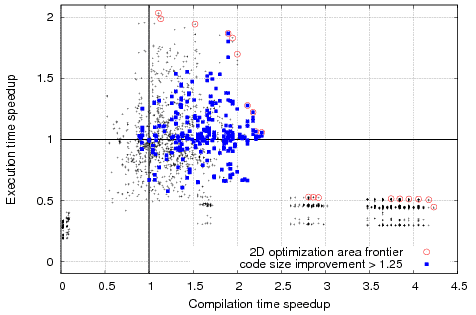
Motivation example:
Example of complex optimization search spaces for susan_c (including optimization space frontier for multi-objective optimizations) from Collective Benchmark after using CCC framework (that has some similarities with the useful ACOVEA tool but also allows automatic sharing of optimization knowledge with the community in the Collective Optimization Database and uses plugins to implement various search techniques besides genetic algorithms) and cTuning CC/MILEPOST GCC 4.4.x:
Example of program similarities using static program features and based on best found program optimizations continuously collected in the cTuning optimization repository that improve execution time (as well as code size, compilation time, etc):
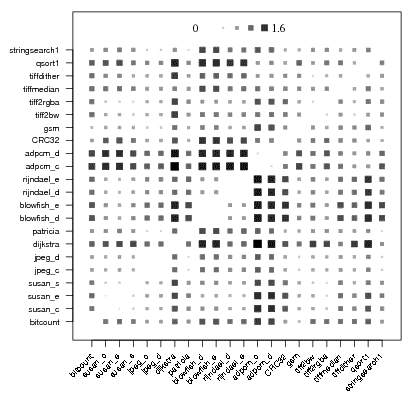
cTuning CC/MILEPOST GCC uses online machine learning and prediction plugins to correlate program features and optimizations on the fly and quickly predict profitable optimizations for a previously unseen program and for multiple user objectives (balancing execution time, code size, compilation time, etc).
Collective Mind framework and repository is the latest development by Grigori Fursin that aggregates all his past R&D to deliver new universal plugin-based framework to systematize and automate computer engineering using crowdsourcing and machine learning.
cTuning foundation (non-profit association run by the community) is the outcome of the EU FP6 MILEPOST project (2006-2009)!