From cTuning.org
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
* '''ccc-comp''' | * '''ccc-comp''' | ||
| + | Command line: ccc-comp <compiler extension> "Compiler optimization flags" "Additional flags that should not be recorded (not optimization related)" | ||
| + | This tools invokes Makefile associated with the compiler extension and compiles program with the specified optimization flags. Then it invokes scripts to send statistics to COD. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''ccc-run''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Command line: ccc-run <Dataset> <Base_line_run_param> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This tools executes application with a given dataset number. If it's the first baseline run (to compare execution time, code size and compilation time improvements, etc with the consecutive iterative feedback-directed runs), the Base_line_run_param should be set to 1, otherwise to 0. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Iterative feedback-directed compilation example === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Directory with applications ''apps'' has one test directory CCC-TEST-APP. You can download the whole CBench and datasets using ''ccc-admin--get-cbench-from-svn.sh'' and ''ccc-admin--get-cbench-datasets-from-svn.sh''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The list of all benchmarks set up for 1 dataset is in file ''ccc--bench-list.dataset1.txt''. The list of all benchmarks with all datasets is in file ''ccc--bench-list.dataset_all.txt''. One of those files should be copied into ccc--bench-list.txt that is the working file with the list of benchmarks to be processed automatically by scripts. | ||
| - | |||
=== Plugins === | === Plugins === | ||
Revision as of 17:31, 26 March 2009
Continuous Collective Compilation Framework documentation
Navigation: cTuning.org > CTools > CCC
This is the first draft of the documentation. It should be updated. Any help is appreciated.
Contents |
License
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as published by the Free Software Foundation.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
If you found this software useful, you are welcome (but not obliged) to reference http://ctuning.org website and these publications FT2009,FMTP2008 in your derivative works.
Framework high-level overview
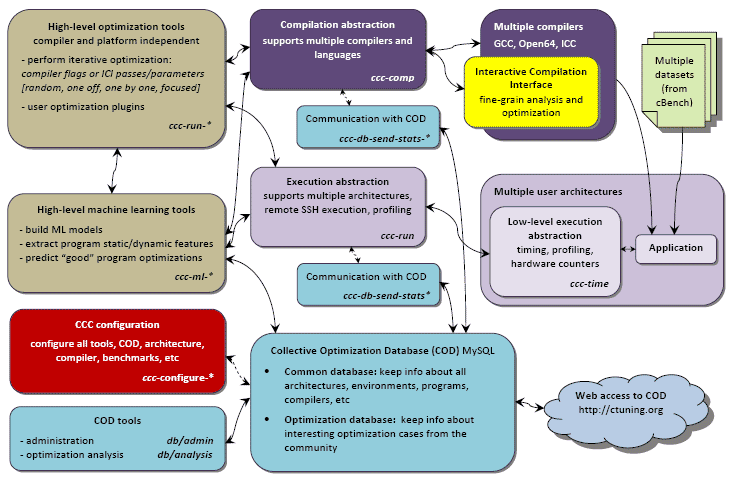
Requirements
To successfully install CCC Framework, you need:
- C/C++ compiler (GCC) (we hope to convert 1 program that uses C++ to C).
- MySQL client and development headers /include/mysql/* (not strictly required but functionality will be reduced).
- PHP (not strictly required but functionality will be reduced).
- PAPI library (not strictly required - used in auxiliary tools).
Directory structure
- /
- README.txt - brief README and GPL license info
- INSTALL.sh - main installation script that calls ccc-configure* scripts one by one
- ccc-configure* - distributed configuration scripts for different tasks (See Installation section)
- ccc-build.cfg - CCC Framework build number
- ccc-build-db.cfg - lower and upper version number of the Collective Optimization Database which this version is intended to work with (to avoid incompatibility when both CCC Framework and COD are evolving).
- /src-plat-dep - platform dependent tools and plugins
- /include/ccc - CCC Framework header files
- /lib - auxiliary functions
- /plugins - plugins sources
- /compilation - iterative feedback-directed compilation plugins
- /ml-prediction - machine learning prediction plugins
- /tools - low-level tools
- /ccc-time - substitution for standard time program to collect different profile info about program including hardware counters support
- /ccc-comp - basic tool dealing with program compilation
- /ccc-run - basic tool dealing with program execution and profiling collection
- /ccc-db-send-stats-comp - send compilation statistics to COD
- /ccc-db-send-stats-comp-passes - send info about compiler optimizations (at function-level) to COD
- /ccc-db-send-stats-prog-feat - send info about program static features (machine learning) to COD
- /ccc-db-send-stats-run - send execution statistics to COD
- /tools-aux - auxiliary tools if system supports that
- /hardware-counters-papi - collecting hardware counters statistics (dynamic program features for machine learning or statistical analysis)
- /src-plat-indep - platform independent tools and plugins
- /include/ccc_script_functions.php - library that supports platform independent plugins and deals mostly with COD
- /plugins - plugins and scripts
- /cfg - CCC configuration directories for different architectures/environments/compilers
- /default - default configurations including optimizations for several compilers (GCC,Open64,PathScale)
- /install - installation directory for (platform-dependent) tools and scripts
- /apps - applications converted to work with CCC and scripts to automate iterative compilation
Installation
Installation is performed using INSTALL.sh script for each platform (architecture/environment) on which iterative compilation experiments will be performed. This script calls individual ccc-configure-* scripts to configure the following:
- ccc-configure-1-platform-name.sh - Select local name of the platform (the directory with this name will be created in cfg and install directories).
- ccc-configure-2-database.sh - Configure Collective Optimization Database access if it is used for experiments. If it is not used, all compilation and execution statistics is recorded in local files and can later be send to database in case you would like to share your optimization cases.
- ccc-configure-2b-database-test.sh - Test COD access using parameters from the previous step.
- ccc-configure-3-platform.sh - Provide architecture info for experiments (you can view if similar already [1] exists and use its unique ID or add new architecture info directly). Each architecture has its unique ID to be able to share optimization cases.
- ccc-configure-4-environment.sh - Provide environment info for experiments (you can view if similar already [2] exists and use its unique ID or add new environment info directly). Each environment has its unique ID to be able to share optimization cases.
- ccc-configure-5-compiler.sh - Provide compiler info for experiments (you can view if similar already [3] exists and use its unique ID or add new compiler info directly). Each compiler has its unique ID to be able to share optimization cases.
- ccc-configure-6-compile-all-plugins.sh - Compile and configure all plugins
- ccc-configure-6-compile-all-tools-aux.sh - Compile all auxiliary tools if platform supports them
- ccc-configure-6-compile-all-tools.sh - Compile all low-level tools
- ccc-configure-7-update.sh - Check for update
- ccc-configure-8-set-environment.sh - Set environment based on the information entered in all previous steps. The environment files ccc-env.sh and ccc-env.csh for your platform will be created in the directory cfg/<platform_name>/. You can edit them to correct paths to specific compilers such as GCC with ICI, MILEPOST GCC, LLVM, Open64, PathScale, Testarossa, Intel, etc.
This script has to be invoked for a given platform before performing any experiments. The ccc-configure* scripts can later be invoked individually if needed.
Collective Optimization Database
COD has been recently separated into 2 parts: common and experimental. The common database keeps information about architectures, environments, compilers, programs, compiler flags, architecture configurations, etc - the information that can be common for many users. The experimental databases keep local information about optimization cases after iterative feedback-directed compilation. They can have user-sensitive information and hence should not always be shared. User can later select interesting optimization cases to share.
Some more info about COD web-services/API is here.
To be extended
Applications
CCC Framework is intended to automate a large number of iterative compilation experiments. Application has to be slightly modified to work with CCC. For example, Collective Benchmark is already prepared to be used directly with the latest CCC Framework. CTools:CBench:Format Here you can find more info about benchmark format. Eventually, we plan to add full support to enable application optimizations transparently without any Makefile modifications.
Low-level tools
There are 3 main low-level tools that abstract platform from iterative compilation experiments:
- ccc-time
Command line: ccc-time -fe <name_of_executable> -fp <command_line_for_executable> -ft <file to save time>
This program substitutes native time to profile program and potentially support different architectural features such as hardware counters, etc. Normally, if users work with ported to CCC Framework applications such as CBench, they will manipulate only with ccc-comp and ccc-run or high-level plugins and will not use this tool directly.
- ccc-comp
Command line: ccc-comp <compiler extension> "Compiler optimization flags" "Additional flags that should not be recorded (not optimization related)"
This tools invokes Makefile associated with the compiler extension and compiles program with the specified optimization flags. Then it invokes scripts to send statistics to COD.
- ccc-run
Command line: ccc-run <Dataset> <Base_line_run_param>
This tools executes application with a given dataset number. If it's the first baseline run (to compare execution time, code size and compilation time improvements, etc with the consecutive iterative feedback-directed runs), the Base_line_run_param should be set to 1, otherwise to 0.
Iterative feedback-directed compilation example
Directory with applications apps has one test directory CCC-TEST-APP. You can download the whole CBench and datasets using ccc-admin--get-cbench-from-svn.sh and ccc-admin--get-cbench-datasets-from-svn.sh.
The list of all benchmarks set up for 1 dataset is in file ccc--bench-list.dataset1.txt. The list of all benchmarks with all datasets is in file ccc--bench-list.dataset_all.txt. One of those files should be copied into ccc--bench-list.txt that is the working file with the list of benchmarks to be processed automatically by scripts.
Plugins
Iterative compilation plugins
Machine learning plugins
Data Analysis plugins